- Data Architecture
- Process Objective: To develop the Data Architecture and describe how to store, process, analyse and make available data and city services.
- Application Architecture
- Process Objective: To develop the Application Architecture and address the interoperability between different applications and city services.
Information Architecture
The Information Architecture process aims to develop the Data and Application Architecture, describing how the city’s Information Systems Architecture will enable the Service Architecture. The Information Architecture describes the interaction of the applications and data of the city. For example, a Smart City dashboard enables city monitoring by displaying real-time data on weather, air pollution, public transportation, delays, public bikes availability , river level, and electricity (Kitchin, R., 2014).
Activities
The Information Architecture lifecycle stage of the Architecture Design Process (see fig. 1) includes the following main activities and subprocesses:
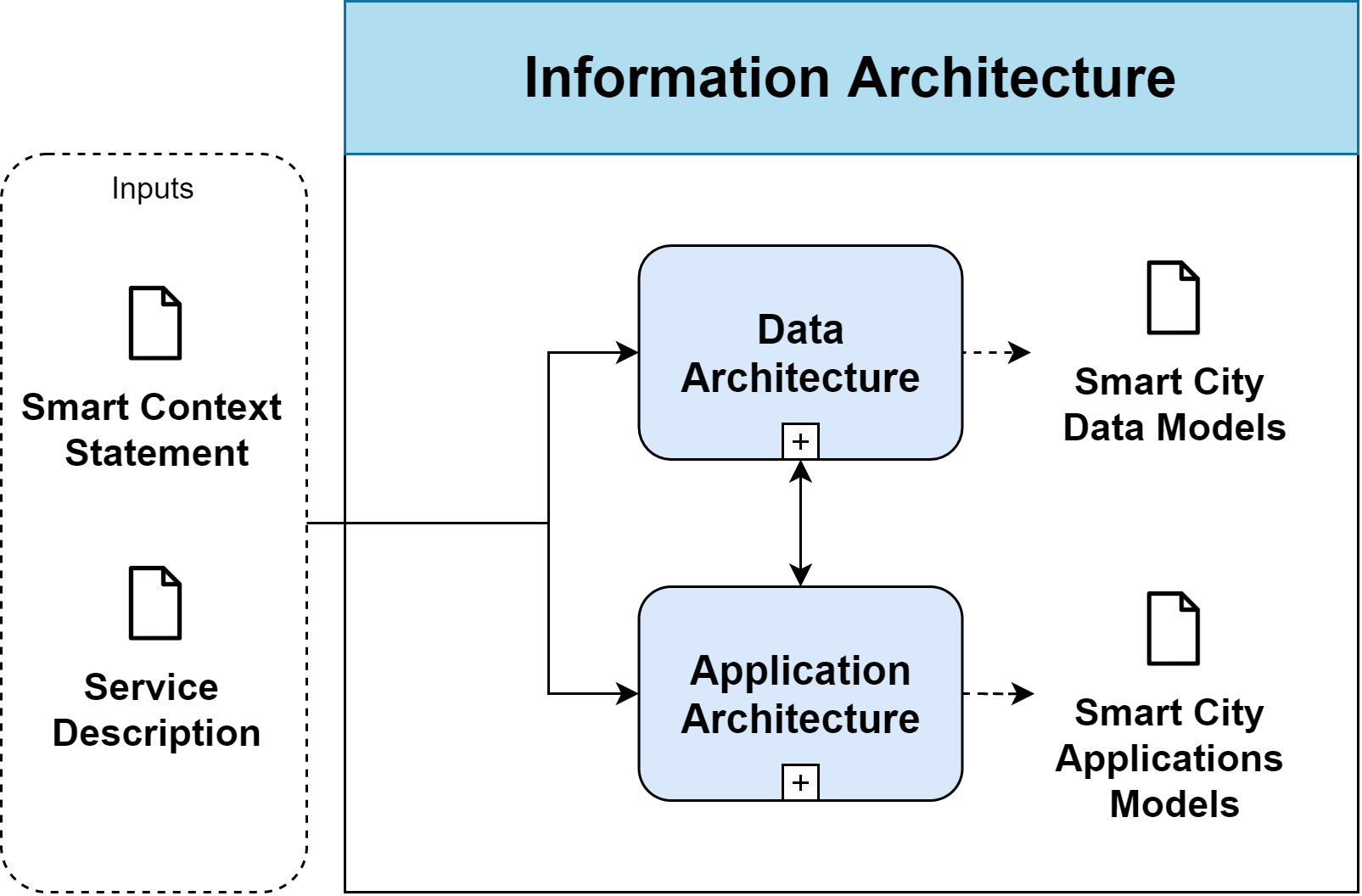
Inputs
- Smart Context Statement
- Consider the existing data and application principles, standards and requirements specification from the Smart Context Definition.
- Service Description
- Consider the existing list of city services and their related architecture concepts (e.g. city actors, contracts, indicators, etc.) from the Service Architecture Definition.
References
- Kitchin, R., 2014. The real-time city? Big data and smart urbanism. GeoJournal, 79(1), pp.1-14.
- The Open Group. “Open Group Standanotepadrd TOGAF Version 9.1”, 2011.